DNA & Inheritance
How the sex cells divide - meiosis
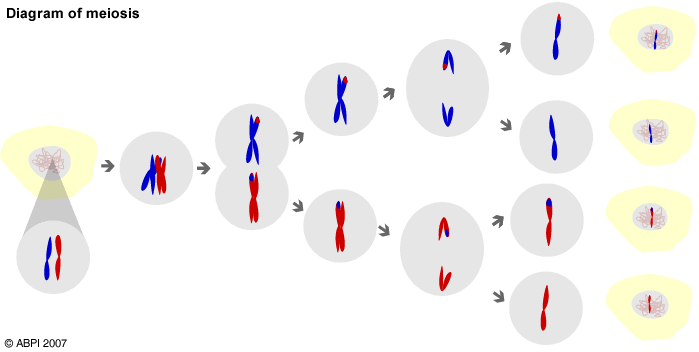
Meiosis is the process by which new cells with half the usual number of chromosomes are produced. In humans the full complement of 46 chromosomes is called the diploid number. Meiosis produces cells with 23 chromosomes, known as the haploid number, and these are the gametes, i.e. sperms for males and ova
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
In meiosis there are two lots of cell division so that a single diploid cell gives rise to four haploid cells. During fertilisation two haploid nuclei join to give a zygote with the diploid number of chromosomes. The zygote then grows and develops by mitosis.
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
How characteristics are passed on

Genetics is the study of inheritance, that is, how characteristics are passed from one generation to the next. Gametes are haploid with only one of each chromosome and therefore one of each gene. When two gametes fuse at fertilisation the zygote now has two of each gene (that is a pair of alleles for each gene) one from the mother and one from the father. Where the alleles are different, one may be recessive and the other dominant and the dominant allele will determine the characteristic.
We can use genetic diagrams to show how a characteristic is passed on. Letters are used to represent the genes and a capital letter means an allele is dominant, and a small letter means a recessive allele. The diagram right shows the possible gametes and offspring for parents who both have homozygous alleles for eye colour, one for blue eyes and one for brown eyes. Note that, any child with Bb alleles will have brown eyes but carries the allele for blue eyes which could be passed on to a later generation.
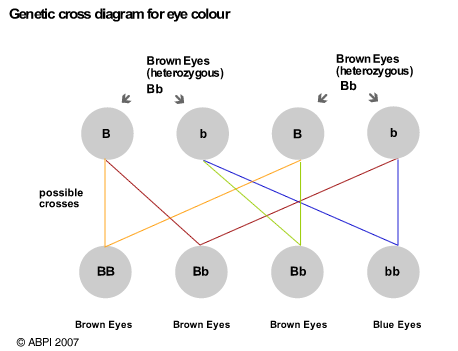
For parents with heterozygous alleles for eye colour, the outcome is different as shown in the diagram below.
The ability to roll the tongue is something an individual can or cannot do and is passed on genetically. It cannot be learned. In the diagram below, the parents are heterozygous for tongue rolling.
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
The inheritance of blood group can be represented by the simplified diagram below. It shows the possible blood groups of offspring when the parents are heterozygous A and heterozygous B.
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
Male or female?
Many characteristics are controlled by a gene (or sometimes a few genes). The gender of the next generation, however, is determined by a whole chromosome. Human chromosome pair number 23 differs between male and female. It can be XX , which is female, or XY, which is male. In the following genetic diagram the letters represent chromosomes.
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
It shows that the ratio of boys to girls is 1:1, that is, there is always an equal chance of getting a boy or a girl.
Question 3
the missing word or phrase to complete the sentence.