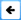DNA & Cloning
How a cell divides - mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells
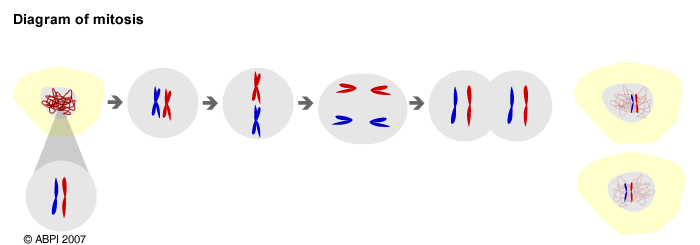
- Firstly, every chromosome makes a copy of itself and each new pair is then called a pair of sister chromatids
- Then the membrane of the nucleus dissolves so that the chromatids spill out into the rest of the cell.
- They then line up across the middle of the cell and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell.
- Now they are called chromosomes again and each set becomes enclosed in a new nuclear membrane.
- Eventually the mother cell splits into two giving rise to two daughter cells each with the same set of chromosomes as the original cell.
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
When an egg has been fertilised, and thus becomes a zygote, it undergoes mitosis, dividing to become two cells, then four, then eight etc. In a human embryo, up to the eight-cell stage all the cells are identical and have the potential to become any kind of cell required by the body. These eight cells are known as embryonic stem cells.
You are a unable to view this animation as you do not have the correct version of Adobe Flash Player installed. Please visit the Abobe website to install the latest version of the free Adobe Flash Player
Cloning in nature

Mitosis occurs in the natural process of growth, but many plants and some animals also use mitosis as a method of reproduction known as asexual reproduction.
The strawberry plant sends a runner out from the main stem and, where this touches the ground, new plants develop from buds on the runner. Spider plants regularly send out drooping branches, which, if they touch the ground, will root and produce new plants. The single-celled amoeba is one of a small number of animals that reproduce asexually. The new plants or animals produced are exact copies of the parents and are known as clones.
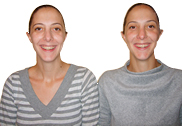
Since identical twins have both developed from the same fertilised egg, they can be regarded as naturally occurring clones.
Artificial cloning
Cloning is a natural process, but scientists have also developed methods of producing clones in an artificial way. Many plants are produced by layering, cuttings and by grafting and budding. Plantlets can also be grown from one original plant by tissue culture. Just a few cells of the plant are treated with hormones in a special environment and many thousands of plants can be produced quickly, disease free and all year round.

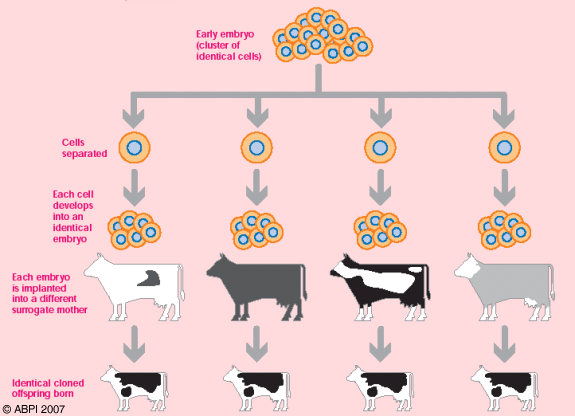
Cloning of animals has also been done. It is quite common, for example, to use the sperm from a prize bull to artificially inseminate selected cows, which have been given hormones to make them produce lots of eggs. The fertilised eggs develop into embryos each of which can be divided to create several identical embryos. These cloned embryos are then implanted into other cows, or they can be frozen and used later. Cloning was also used in the case of Dolly the sheep, which was the first mammalian clone produced from one adult cell.